Industry 4.0 (or Industrie 4.0 in German) is a term that was first invented by Professor Wolfgang Wahlster, CEO and Scientific Director of the German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI) in 2011. The term also was announced by Mrs. Angela Markel, the head of Germany government, that Germany was the first nation to make the fourth industry revolution. Industrie 4.0 is one among several projects under the High-Tech Strategy 2020 that Germany government will invest in this near future. The goal is to make the country a leader in technology to strengthen its competitiveness for both the economy and the industry.
Industry 4.0 is making the production process connected with information technology or making its own access inseparable to information technology. For instance, the system input used to produce consumer goods orders directly through online communication tools. Put the transmission in consumer electronic devices to process usage statistics and automatic notification to the factory where the appliance is damaged, expired or needs maintenance. In health care area, edible miniature computer (equivalent size to tablets) has been used for collecting health-related data in the human body.
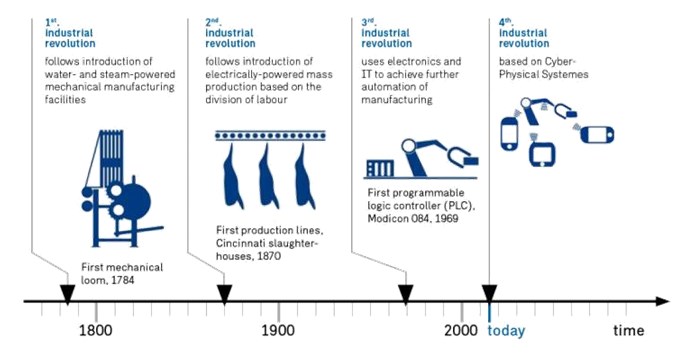
The fourth Industrial revolution has been revolutionized after the wide spread of the third generation (Digital Revolution) in Germany, which highlighted the impact of information and computer technology on the economic potential and financial optimization. The increasing capacity in computer and electronic industry caused other high technology industry blossomed such as biological and genetic industry and nanotechnology and material science industry. The second industrial revolution focused on the production of large quantity of products using machinery or electronic equipment that utilized electrical power sources. Industries such as the automotive industry, processing of agricultural raw materials, and military armaments industry were developed in this era.
Characteristics of the fourth industrial revolution
The fundamental principles of industry 4.0 that makes a distinction between the fourth age of industrial revolutions and the others are as follows:
- The ability to collaborate between man and machine (Interoperability) – this era of industry revolution focuses on providing seamless interoperability between man and machine and the interaction between them in the manufacturing process. Both sides rely on communication technology called the Internet of Things (IoT).
- The production process can be seen clearly from the virtual image of the plant (Virtualization) – the virtual image of the plant will be built by simulating the process of thoroughly linked via smart sensor devices attached to machines or equipment in the production process. The objective is to keep the production process as much automatically linked together and as clearly visible as possible through a system called Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS).
- Decentralized control scheme (Decentralization) – the capability of CPS that enables staff in the factory can make decisions quickly. The objective is to decentralized decision making in machine control and resolving problems quickly and accurately.
- Real-Time Capability is focusing on the capability of manufacturing processes that makes instant decisions through the communication system via the network backbone. This enables the industry to reduced inventories or work-in-process materials required during the process, as well as waste and down time of the machine.
- Model that emphasizes service (Service Orientation) – the innovative service model of information system called Internet of Services (IoS) is used to control the monitoring and analysis of data collected from the smart sensor devices. The service focuses on the system’s ability to produce products to meet the needs of individual consumers. That is the Flexible manufacturing process has been created.
- The ability to separate (Modularity) – is a unique feature of the flexible manufacturing system. The production process can be separated from each other to overcome the complexity of a system or a long-line production process. Long-line or continuous production process is broken down to make management easier. The ability to separate also means the plant is able to modify the machines or manufacturing process to meet the diverse needs of consumers more quickly.
The aforementioned characteristics of the fourth industrial revolution are also based on the following physical infrastructure of the industrial system, which transforming factory into “Intelligent Factory”:
- Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) represents the nature of the link between the machines. The information technology systems, especially smart sensor devices and network backbone, create a transmission and storage of the physical characteristics of machines and their associate physical conditions. Through a network of smart sensor devices, the machines are allowed to talk to each other to create the smooth production process. The result of real-time capability via the screen of a virtual factory is the capability of the CPS system. There are other terms used that related to CPS such as Machine-to-Machine (M2M), Human-Machine Interactions (HMI), Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC) and the Smart Grid.
- Internet of Things (IoT) is a hardware device that acts as the connecting of each machine or device through the Internet. It may be a signal transmission, receiver, or both. Each hardware device may be transmit or receive short-term or long-term signal depending on the type of device. This device is based on a technology called “Intelligent Sensors.” At present, there are many thousand types of intelligent sensors, including tracking sensor, reporting environment (Awareness sensor), conduct a preliminary analysis to aid decision (Analytic sensor), examination and measuring sensor, control sensor, automatic responding sensor and so forth.
- Internet of Service (IoS) is the concept of using the internet network and its software in providing service, also known as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) which imply an information infrastructure as a service to end users. The resulting optimization reduces the time and cost of operations. IoS focuses on infrastructure-related technologies, including cloud computing and other network infrastructure platforms. Information technology infrastructure designer is crucially aware the Big Data phenomenon after the introduction of intelligent applications and smart sensor devices.

Thailand and The fourth industrial revolution.
Thailand is a country where industrial development is based on agriculture products, food processing, textiles and apparel, plastics and chemicals, as well as automotive parts and electronics. Their industrial processes focus on the mixture of machinery and labor to produce in large quantities but low variety of products. Some industry started to introduce information technology and computer applications while some others were widely adopt such technology long enough. Most industries in the country are in the transitional stage from the second industrial era to the third era in the near future. However, considering the potential advancement to the fourth era, there are many challenges including issues of technology development in the country, skilled labor shortage, the quality of education which is fundamental to the production of high skilled personnel, labor cost does not correspond to the quality of the current workforce, which resulted to many industry cannot increase productivity and improve performance. As mentioned above, there are major obstacles that encumber industrial development into the fourth era.
However, the analysis showed that Thailand has a chance to advance the industry to the fourth era because the country is highly accept technology and learn to use the technology quite well. The level of technology adoption and diffusion of knowledge will cause an increase of the technology readiness level of the country. This includes an investment on IT infrastructure that is the basis for information technology and other technologies utilization. Moreover, the features of the technology in the fourth era has the characteristic of the “Leap Frog”, which means there is no need to develop technology step by step to get to the goal but such proven technology could be acquired instantly through the redesigning of the manufacturing process. This requires a careful planning and design process by experts.
Another important opportunity for Thai industry is the fact that the underlying technology in the fourth era of industrial revolution is primarily based on computer and information technology. According to Moore’s law that the price of this kind of technology is usually drop below 50 percent in every two years, this is a great opportunity for small and medium size industry which accounted the largest proportion (more than 90 percent) of the country’s total industry. This also predicted that small and medium industry is able to access to such technology in the next few years. Modular manufacturing design is also another important aspect that makes small and medium industry to adopt only to their priority process to reduce problems and inefficiency and to become partial automated factory.
The rate of technology adoption in the fourth era is a giant leap into the future. Same as ICT, such as smart phone and computer tablet, technology in the fourth era has been proven by the developed countries as being successful in enhancing productivity and reducing resource utilization. The replication of the success stories and further development (Copy & Develop) in developing nations are expected to vastly deployed. It was also predicted that this is a chance for Thailand to develop a quantum leap for the industry. However, country needs to prepare seriously on the production staff, researchers and workers who have basic knowledge of the technology and manufacturing process in order to become fully industrialized countries in the future.

